Understanding Acute Pain: A Common and Persistent Problem
Acute pain is a universal human experience that affects individuals of all ages, backgrounds, and walks of life. It is a subjective sensation that is characterized by a sudden and intense burning, aching, or throbbing sensation in a specific area of the body. Acute pain can be caused by a wide range of factors, including injury, surgery, infection, and certain medical conditions.
Acute pain is a normal response to tissue damage or inflammation, and it serves as a vital warning system that alerts the body to potential harm. However, for many individuals, acute pain can become chronic, persistent, and debilitating, significantly impacting daily life and quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of acute pain, exploring its causes, effects, treatment options, and ways to manage and overcome it.
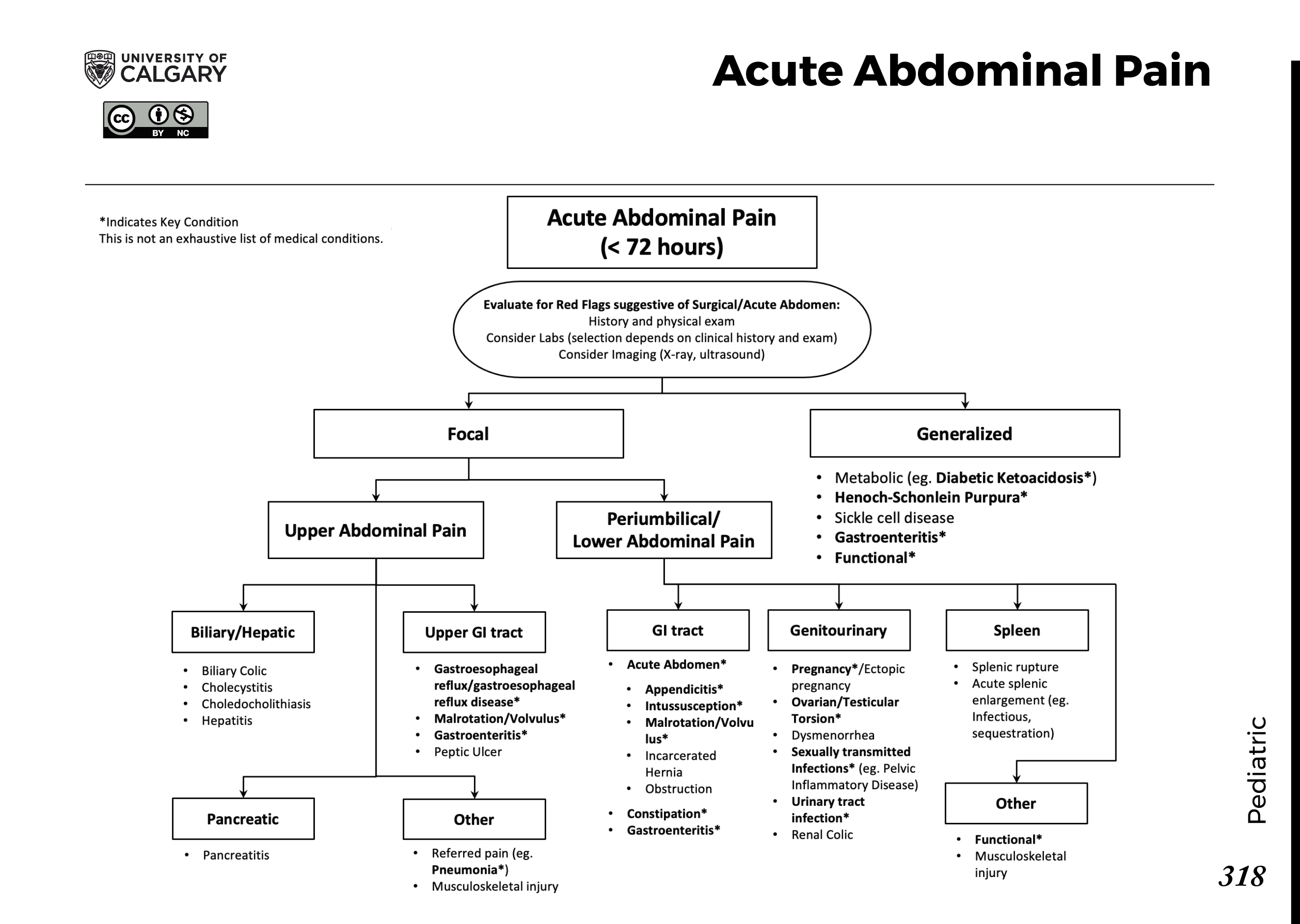
Types of Acute Pain
Acute pain can be classified into several types, including:
- Somatic pain: This type of pain is caused by tissue damage or inflammation and is typically felt in specific areas of the body, such as the back, arms, or legs.
- Visceral pain: This type of pain is caused by damage to internal organs and is often felt in the abdomen, chest, or pelvis.
- Neuropathic pain: This type of pain is caused by damage to the nervous system and is often characterized by shooting, burning, or tingling sensations.
Some common causes of acute pain include:
- Injury or trauma: Acute pain can be caused by injuries such as sprains, strains, or broken bones.
- Surgery: Pain is a common side effect of surgery, particularly if the surgery involves significant tissue damage or cutting.
- Infection: Acute pain can be caused by infections such as appendicitis, meningitis, or endocarditis.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as cancer, fibromyalgia, or arthritis, can cause acute pain.
Effects of Acute Pain
Acute pain can have significant effects on an individual's physical and mental health, including:
- Physical limitations: Acute pain can limit physical activity and mobility, making it difficult to perform daily tasks or engage in enjoyable activities.
- Mental health impacts: Acute pain can lead to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Sleep disturbances: Acute pain can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and other related problems.
- Social withdrawal: Acute pain can cause individuals to withdraw from social interactions and relationships.
Treatment Options for Acute Pain
Treatment options for acute pain depend on the underlying cause of the pain, as well as the individual's medical history and personal preferences. Some common treatment options include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, as well as prescription medications such as opioids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Lifestyle modifications: Making changes to daily routines, such as taking regular breaks, engaging in physical activity, or practicing relaxation techniques.
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, massage, or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may be effective in managing acute pain.
- Surgical interventions: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve acute pain, such as spinal surgery or organ transplantation.
Managing Acute Pain at Home
Managing acute pain at home requires a multi-faceted approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies, and pain management strategies. Some tips for managing acute pain at home include:
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids to help reduce pain and discomfort.
- Taking regular breaks: Resting and relaxing regularly to reduce fatigue and stress.
- Engaging in physical activity: Gentle exercises such as yoga or walking to promote relaxation and reduce pain.
- Practicing relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation to reduce stress and anxiety.
Acupuncture for Acute Pain
Acupuncture is a form of traditional Chinese medicine that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate healing and relaxation. Acupuncture has been shown to be effective in managing acute pain, particularly for conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and migraines.
Some benefits of acupuncture for acute pain include:
- Reduced pain intensity: Acupuncture can help reduce the intensity of pain, allowing individuals to engage in daily activities with greater ease.
- Improved mood: Acupuncture can help reduce stress and anxiety, promoting a sense of well-being and relaxation.
- Enhanced sleep quality: Acupuncture can help improve sleep quality, reducing fatigue and other related problems.
Living with Chronic Pain
Living with chronic pain can be challenging and isolating, but there are ways to manage and overcome it. Some strategies for coping with chronic pain include:
- Connecting with others: Joining support groups or talking to friends and family members to reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Practicing self-care: Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as yoga or meditation.
- Seeking professional help: Consulting with healthcare providers or pain management specialists to develop a personalized treatment plan.
- Focusing on activities that bring joy: Engaging in hobbies or activities that promote happiness and fulfillment.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Chronic Pain
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. CBT has been shown to be effective in managing chronic pain, particularly for individuals who experience anxiety or depression.
Some benefits of CBT for chronic pain include:
- _
Maureen Bates
Travis Kelce Health
Competition Rank Tracker
Article Recommendations
- Chaun Woo Parents Nationality
- Competitiveeo Rank
- Yumieto
- Rick Harrison Net Worth
- Is Justin Bieberead
- Mamitha Baiju
- Who Is Brittany Forcengaged To
- Matt Czuchry Relationship
- Michael Boulos
- Does Gloria Borger Have Cancer